Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
Today, endoscopic Sinus Surgery ( ESS ) is one of the most applied surgeries that is performed mainly in the treatment of chronic sinus inflammations, sinus tumors, injuries of the anterior cranial base, eyeball injuries related to trauma, and pressure on the eye nerve. At the same time, it is preferred to be used in the drainage surgeries of the lacrimal sac ( Dacryocystorhinostomy ) and in the surgical treatment of some pituitary gland adenomas ( Endoscopic hypophysectomy ) in gradually increasing ratios.
Due to narrow, complex anatomy of the regions in which sinuses around the nose are located, and due to the important neighboring organs like the brain, eyes, eye nerves, lacrimal sac, carotid arteries make training, experience and the highest technical skill with a small error of margin essential in Endoscopic sinus operations.
In chronic sinus diseases, with ESS mainly the below specified operations are performed;
Removal of inflamed tissues/polyps
Opening and dilation of the drainage canals that connect the sinuses to the nose
The correction of anatomical problems like concha bullosa, more than one drainage holes (accessory ostium) and abnormal mucosa contact regions.
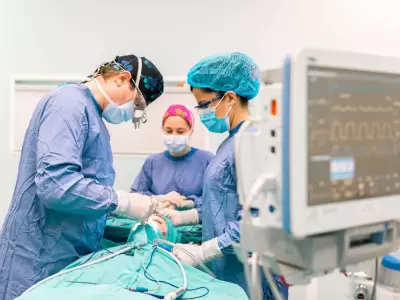
During ESS, in cases in which advanced technological devices are especially used like surgical navigation, balloon sinuplasty or microdebriders, general anesthesia is preferred for the comfort of the patient and the surgeon. The duration of the surgery varies according to the extent of the pathology and to the presence of additional interventions like the correction of intranasal deviation, aesthetic nose surgery, concha reducing and anatomical variations. While the intervention to a single sinus lasts for approximately 15 minutes, the surgery for pathology involving all sinuses may exceed two hours.
If a necessity does not occur related to additional interventions like submucosal reducing of the nasal turbinates, intranasal packings are not placed after the surgery, and the patients may breathe comfortably from the nose. Special packings and various materials that are placed in to sinuses in order to prevent bleeding or adhesions at the end of the operation do not effect breathing from the nose.
After the surgery, complaint of serious pain does not occur, simple pain killers are generally enough.
Though the patients are recommended to stay at the hospital at the day of the surgery, they may be discharged on the same day according to the content of the operation.
After the surgery, antibiotic administration is recommended at least for 10 days, this period may be prolonged or additional medications may be added when it is necessary. Sprays containing sterile saline that clean the nose mechanically and moisten the nose should be used till the end of crust formation in the nose. In patients with allergy or polyp, cortisone containing sprays and medications that decrease the risk of polyp formation are recommended after the surgery. In patients suspected to have allergic fungi sinusitis, are recommended to receive oral antifungal treatment as well.
After the surgery, endoscopic wound care is performed for 3-4 times. During the second visit that is applied at the end of the second week a detailed procedure is performed, the rinds that have formed in the nose and the sinus drainage canals are cleaned, if materials that prevent adhesion were placed in the sinuses, they are removed and wound infection is evaluated. The performance of this comprehensive wound care is very important in respect to the long term success of the operation. Patients have to come back for control visits with intervals of 7-10 days till the completion of recovery according to the extent of the operation.
In some special conditions, the level of difficulty in ESC increases with increase in failure and complication rates accordingly. These special conditions are;
Excessive bleeding in tissues during the surgery
Presence of excessive inflammation
Surgeries of tumors that are especially rich in vascularization
Hypertension
Coagulation disorders (Bleeding diasthesis) / Usage of aspirin
Surgical trauma
The change in the anatomy due to previous operation / trauma
Formation of hard scar tissue due to previous operations
Widespread polyps
Paranasal tumors in / out of he sinuses
Anatomical changes (variations)
Operations directed to posterior ethmoid, sphenoid, frontal sinuses.
During or after ESC, some minor and major complications can be encountered. The most important ones among these are:
Active bleeding
Intraorbital (intraocular) bleeding
Rupturing of carotis
Trauma of the Orbit
Endophtalmitis
Movement disorder in the eye
Nasolacrimal canal (lacrimal sac) trauma
Leakage of cerebrospinal fluid
Intracranial complications
Abscess
Meningitis
Pneumocephaly
Pituitary gland damage.
Computer Aided Sinus Surgery (Surgical Navigation)
Surgical navigation technology enables the following of the location of the surgical equipment within the sinus anatomy on the images of sinus tomography that have been acquired before the surgery, with the help of a special device and a software in real time, in three dimensions and with a margin of error about 1 mm (Figure. 1).
It provides safer application of endoscopic sinus surgery, safer access to all diseased locations and increases the success rate of the surgery to a significant extent and is also useful in special cases with high risk of complication in the elimination of this risks. (see: Surgical Navigation )
The Cost of Surgery In endoscopic sinus surgery, many variables are present that determine your cost of surgery, among these are:
The scope of the operation to be performed: single sided, double sided surgery
Special sinuses to be intervened: Frontal sinus, sphenoid sinus
Surgery method: Standard surgery, surgery with balloon sinuplasty method, combination surgery
Advanced technology to be used: Surgical navigation (computer aided surgery), Microdebrider (shaver)
Special materials to be used: Pureregen Sinus Gel etc.
Other surgeries that have to be/ that are wanted to be performed simultaneously: Reducing of concha, deviation surgery, aesthetic nose surgery etc.
Additional materials and technologies to be used in the additional surgery: Radiofrequency, nasal splints etc.
The hospital in which the surgery will be applied.





Comment
Your Contact Information will not be shared in any way. * Required Fields